Diseases Spread by Cockroaches
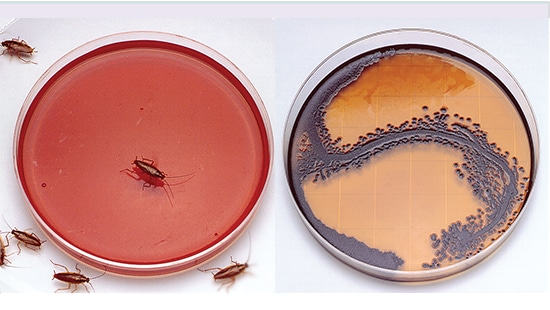
Cockroaches present a significant risk to food safety due to their ability to vector and spread diseases. They contaminate food and food-handling surfaces via their droppings or mechanical transfer from their bodies. On the left are German cockroaches on a petri dish. On the right are colonies of E. coli transferred by the cockroaches.
Contaminating Food and Food-Handing Surfaces
According to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the German cockroach is a known vector for diseases including:
- Salmonellosis – Salmonella food poisoning causes diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps within 12 to 72 hours. Symptoms are generally mild, but can be severe, especially for those with a compromised immune system.
- Staphylococcus infections – This gastrointestinal illness develops soon after food is eaten and usually last about a day. The toxins are heat resistant so are not destroyed by cooking.
- Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria normally lives in the intestines of people and animals and some types can cause illness with diarrhea.
- Typhoid fever – This life-threatening illness is caused by Salmonella Typhi. When a contaminated food is consumed, the bacteria multiply and spread into the bloodstream.
- Gastroenteritis – inflammation of the stomach and small and large intestines, generally leading to vomiting or diarrhea.
General diarrhea.
People may become infected with any of these by eating or drinking a contaminated food or beverage. Cockroaches can also trigger asthma and other allergies.
Learn more about Types of Cockroaches.
More Resources

The Dangers of Cockroaches
Learn how cockroaches can affect food safety.

Types of Cockroaches
Learn about common species of cockroaches most commonly found in commercial kitchens and food handling facilities.

Tips for Pest Prevention
Get proactive pest prevention tips for your commercial kitchen.


